|
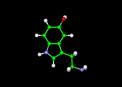
| Serotonin Molecule |
|
| Photo Courtesy by: www.worldofmolecules.com/ emotions/serotonin.gif |
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter. A neurotransmitter is a chemical messenger that transmits nerve impulses
across a synapse in the brain. Serotonin has many roles. It may control one's mood or personality, appetite, sleep, learning,
depression, memory, behavior, muscle contractions, cardiovascular function, and endocrine regulation. For example, melatonin
is made from serotonin and is a hormone that induces sleep. As more melatonin is made, less serotonin is available. The
best way to raise serotonin levels is to eat carbohydrates which produces trytophan which is what serotonin is made of. Serotonin
levels have a large effect on behavior. Serotonin is therefore highly linked with a number of disorders. Those with high
serotonin levels are more likely to be extremely tidy and cautious, such as those with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Those
with low levels of serotonin are usually impulsive or depressed.
|